Derivative contracts play a crucial role in financial markets since they provide hedging and speculation tools. The most widely used contracts among these are futures and forward contracts. You can make better decisions if you know how they differ and what they have to offer. Therefore, in this article, we will explore the advantages of future contracts over forward contracts. We’ll cover various aspects such as standardization, liquidity, counterparty risk, transparency, and more. As a result, you’ll understand why financial markets often prefer futures contracts.
What are Futures Contracts?

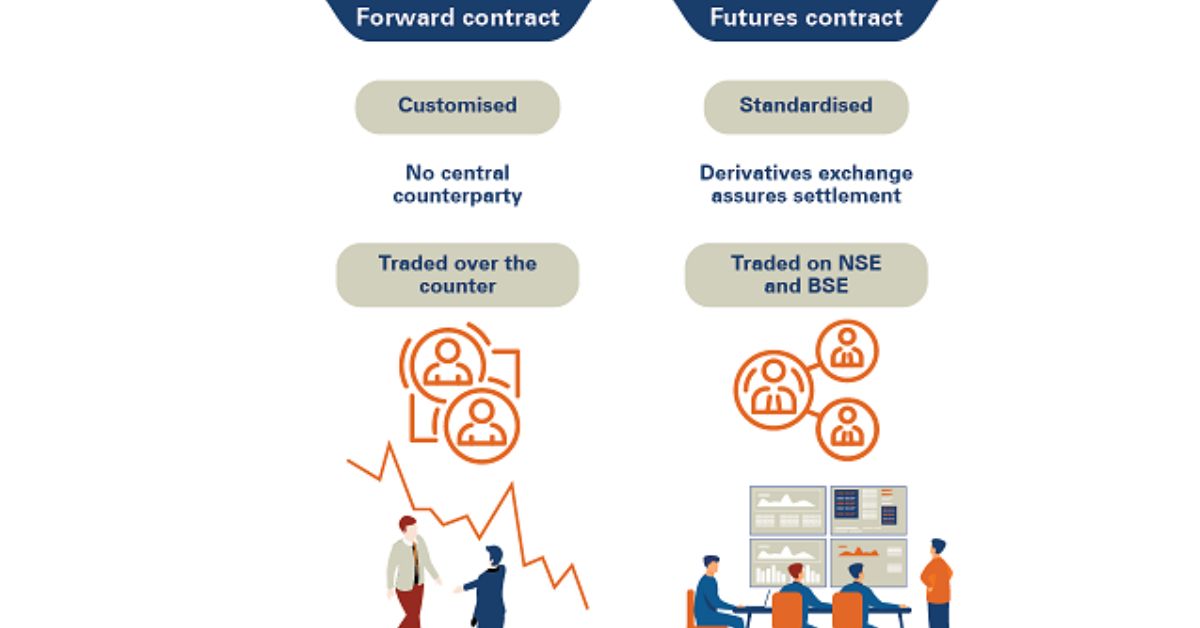
Futures contracts are standardized agreements to buy or sell an asset at a set price on a future date. These contracts are traded on regulated exchanges, ensuring transparency and liquidity. Futures cover various assets, including commodities, currencies, and financial instruments.
The standardized nature allows for easy trading, helping participants hedge against price fluctuations or speculate on future movements. Futures contracts require daily settlement, minimizing credit risk between parties.
What are Forward Contracts?
Forward contracts are customized agreements between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specific price in the future. Unlike futures, forwards are traded over-the-counter (OTC), allowing flexibility in terms and conditions.
This customization can lead to lower liquidity, as each contract may differ. Forward contracts also carry higher counterparty risk since they lack clearinghouse backing. Businesses and investors commonly use forwards to hedge against price volatility in specific assets.
Advantages of Futures Contracts Over Forward Contracts
Futures contracts offer several distinct advantages over forward contracts. In the following sections, we will explore these advantages in greater detail.
1. Standardization and Liquidity
Futures contracts are highly standardized, which enhances their appeal in the financial markets. Standardization means all contracts have uniform terms, including contract size and expiration dates. This uniformity simplifies trading and enables easier comparison between contracts.
Due to their standardized nature, futures contracts tend to attract a larger pool of participants. High trading volume leads to increased liquidity in the futures market. Liquidity is crucial because it allows traders to enter and exit positions with minimal price impact.
In contrast, forward contracts are customizable but lack the same level of liquidity. Each forward contract can have different terms, making them less tradable. This customization often results in wider bid-ask spreads, increasing trading costs for participants.
The high liquidity of futures contracts generally leads to tighter spreads and more efficient pricing. As a result, market participants benefit from better execution prices when trading futures. Overall, the standardization and liquidity of futures contracts provide significant advantages for hedgers and speculators alike.
2. Counterparty Risk Mitigation
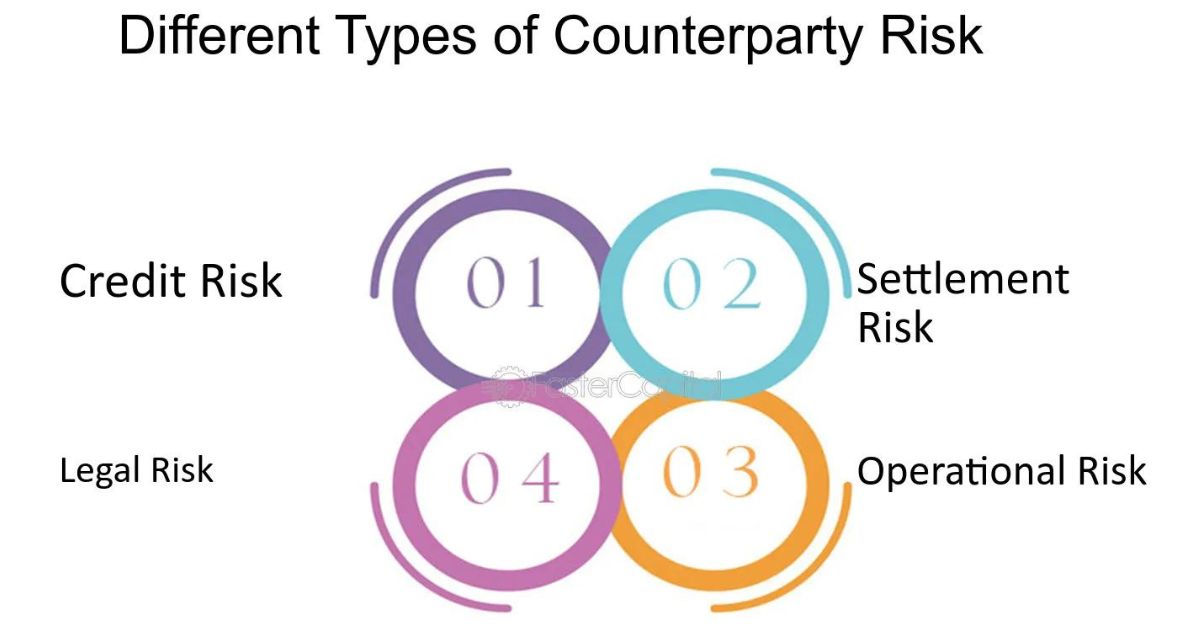
Counterparty risk refers to the possibility that one party in a transaction may default on its obligations. Futures contracts help mitigate this risk through the use of clearinghouses. A clearinghouse acts as an intermediary between buyers and sellers, ensuring that both parties meet their obligations.
When a futures contract is traded, the clearinghouse becomes the counterparty to both sides of the transaction. This arrangement significantly reduces the risk of default, as the clearinghouse guarantees the trade. Participants must maintain margin accounts, which require them to deposit funds to cover potential losses.
Initial margins are set when the contract is created, while maintenance margins are monitored throughout the trade. If the market moves against a trader, they may receive a margin call, requiring additional funds. This daily settlement process, known as mark-to-market, ensures that profits and losses are accounted for promptly.
In contrast, forward contracts are often negotiated directly between parties without a clearinghouse. This lack of an intermediary increases counterparty risk, as there’s no guarantee that either party will fulfill their obligations. If one party defaults, the other may face significant financial losses.
Futures contracts mitigate counterparty risk, offering traders and investors greater security. As a result, they make an excellent choice for managing risk in volatile markets.
3. Transparency and Regulation
Futures contracts are traded on regulated exchanges, providing a high level of transparency. This transparency is crucial for market participants to make informed decisions. Traders can easily access real-time price information, trade volumes, and open interest data.

The regulatory framework governing futures markets helps protect participants from fraud and market manipulation. Regulatory bodies, such as the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the U.S., oversee trading activities. These regulations ensure that all market participants operate on a level playing field.
In contrast, forward contracts are traded over-the-counter (OTC), resulting in less transparency. Since these contracts are privately negotiated, market data is not readily available. This lack of visibility can create uncertainty and lead to potential disputes between parties.
Transparency in futures markets fosters trust among participants, which is essential for market stability. It also encourages more participants to engage in trading, further enhancing liquidity.
Moreover, the regulatory oversight of futures contracts promotes responsible trading practices.
This oversight helps maintain fair pricing and reduces the likelihood of systemic risks in financial markets. Overall, the transparency and regulation of futures contracts contribute significantly to their advantages over forward contracts.
4. Flexibility in Trading Strategies

Futures contracts offer a wide range of trading strategies for market participants. Traders can use various approaches, such as hedging, speculation, and arbitrage, to maximize their returns. This versatility makes futures contracts attractive to both individual and institutional investors.
The standardization of futures contracts allows for easy combination with other financial instruments. For example, traders can create complex strategies by combining futures with options or other derivatives. This flexibility helps participants tailor their strategies to specific market conditions or risk tolerances.
Additionally, futures contracts have multiple expiration dates, providing further flexibility. Traders can choose contracts that align with their investment horizons and market outlooks. This variety allows for short-term and long-term trading strategies.
Moreover, futures markets are accessible to a diverse range of participants. Retail investors, institutional traders, and corporations can all use futures contracts for their specific needs. This accessibility enhances the overall liquidity of the market, benefiting all participants.
In contrast, forward contracts are less flexible in terms of trading strategies. Customization may limit their application in specific techniques. Overall, the flexibility in trading strategies offered by futures contracts provides significant advantages, enabling participants to adapt to changing market dynamics.
5. Cost Efficiency
Futures contracts often exhibit greater cost efficiency compared to forward contracts. Trading futures usually incur lower transaction costs, primarily due to their standardized nature. The high liquidity in futures markets leads to narrower bid-ask spreads, reducing the costs of entering and exiting trades.
Since futures contracts are traded on exchanges, there are typically fewer fees associated with transactions. Brokers often charge lower commissions for trading futures due to the high volume of trades. This cost efficiency allows traders to maximize their returns on investment.
In addition to lower transaction costs, futures contracts offer advantageous margin requirements. Traders can control larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital through the use of margins. This leverage can amplify potential returns while also managing risk effectively.
On the other hand, forward contracts can incur higher costs due to their customization. Negotiating the terms of a forward contract may require legal and administrative expenses, making them more costly. The lack of liquidity in forward contracts can also lead to wider spreads, increasing trading costs.
Overall, futures contracts’ cost efficiency provides a significant advantage for traders and investors. This efficiency enables participants to execute their strategies more effectively, enhancing their overall profitability.
6. Accessibility and Market Participation

Futures contracts are highly accessible to a wide range of market participants. They can be traded by individual retail investors, institutional traders, and corporations alike. This broad accessibility will make future markets vibrant and competitive, benefiting all participants.
The standardized nature of futures contracts simplifies the trading process. Traders do not need extensive knowledge of contract specifics, as terms are uniform across the market. This simplicity encourages new participants to enter the market, increasing overall participation.
Additionally, futures markets offer 24-hour trading, allowing participants to react quickly to global events. This continuous access enables traders to capitalize on price movements at any time, enhancing market efficiency.
The availability of diverse futures contracts across various asset classes also boosts accessibility. Participants can trade commodities, financial instruments, and even cryptocurrency futures, catering to a wide range of interests.
Conversely, forward contracts are often less accessible due to their OTC nature. Negotiating customized agreements may require legal expertise and significant time investment, deterring some participants. The ease of participation in futures markets provides substantial advantages for traders and investors.
7. Hedging Capabilities
Futures contracts provide robust hedging capabilities, making them essential for risk management. They allow businesses and investors to protect themselves against price fluctuations in underlying assets. This hedging ability is crucial for industries that rely on commodities, such as agriculture and energy.
By entering into a futures contract, participants can lock in prices for the future. This price certainty helps businesses budget effectively and stabilize cash flows. Farmers, for example, can secure prices for their crops, protecting against adverse price movements.
Moreover, futures contracts are highly liquid, enabling effective hedging strategies. Traders can quickly enter and exit positions to adjust their hedges as market conditions change. This liquidity is vital for managing risk dynamically in volatile markets.
Additionally, futures contracts cover a wide array of underlying assets, enhancing their hedging effectiveness. Participants can hedge against commodities, currencies, interest rates, and stock indices, providing flexibility in risk management strategies.
Alternatively, forward contracts may offer less effective hedging due to their customization. The lack of liquidity and standardization in forward contracts can hinder timely adjustments to hedges. In general, futures contracts are a good choice for managing risk because of their superior hedging capabilities.
FAQs
What would be one of the significant advantages of Futures contracts?
One significant advantage of futures contracts is their liquidity. Futures contracts are traded on regulated exchanges, attracting a large number of participants. This high trading volume ensures that buyers and sellers can quickly enter and exit positions. Liquidity reduces transaction costs and tightens bid-ask spreads.
Consequently, traders can execute trades at more favorable prices. Additionally, the ability to quickly adjust positions makes it easier to manage risk. Overall, the liquidity of futures contracts provides significant advantages for market participants, enhancing their trading experience and efficiency.
What are the advantages of options over forwards and futures?
Options offer several advantages over forwards and futures contracts. First, options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset. This feature allows traders to limit potential losses while retaining upside potential. Second, options can be used for flexible hedging strategies, allowing participants to manage risk effectively.
Additionally, options have various strike prices and expiration dates, offering more customization. This flexibility enables traders to tailor their strategies to specific market conditions. Furthermore, options often have lower initial costs compared to futures, as they require only a premium payment. Overall, options provide greater strategic flexibility and risk management capabilities.
Is a forward contract more flexible than a futures contract?
Yes, a forward contract is generally more flexible than a futures contract. Forward contracts are customized agreements between two parties that allow them to negotiate specific terms. This customization can include contract size, expiration date, and the underlying asset’s price.
In contrast, futures contracts are standardized and traded on exchanges, which limits flexibility. The terms of futures contracts are set by the exchange, making them uniform across all trades. This standardization facilitates liquidity but reduces customization options.
Read More: Top 7 Crypto Futures Trading Apps
The Takeaway
Futures contracts stand out for their unique advantages, including transparency, accessibility, and diverse trading strategies. These features empower traders to make informed decisions and adapt to market changes effectively. Additionally, the regulatory environment surrounding futures markets ensures fair practices and stability.