Traders and investors need to understand market structures. One key concept is whether to deal with contango or backwardation in futures markets. Each market condition has its implications and strategies. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between contango and backwardation. Let’s talk about their impact on trading strategies and which might be best for your goals.
What is Contango?
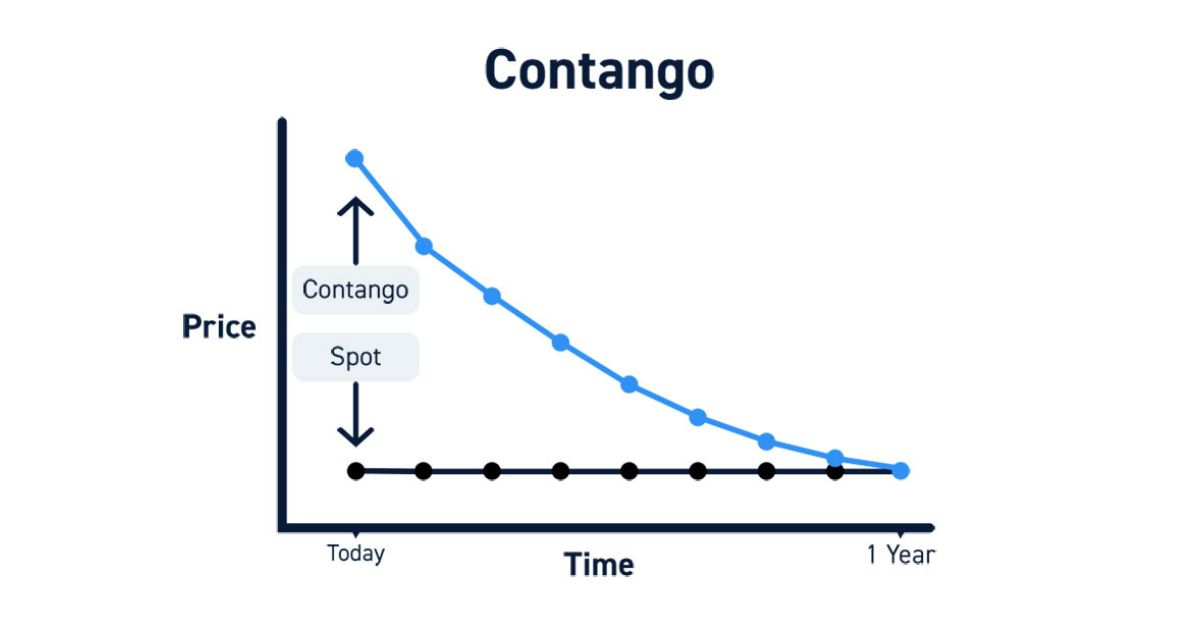
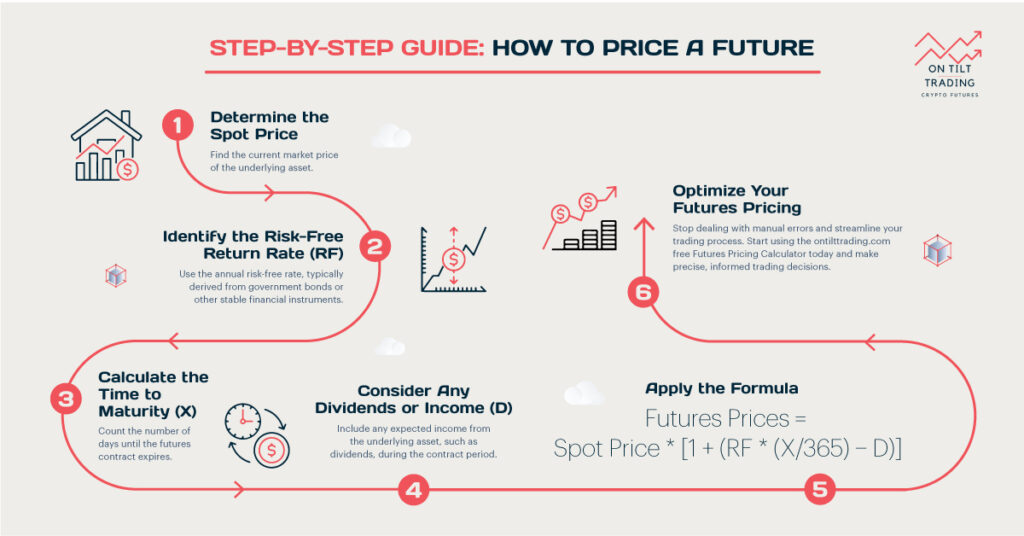
Contango is a market condition where futures prices are higher than the spot price. This situation indicates that traders expect prices to rise. For example, if the current oil price is $50 per barrel, but futures are $55, the market is in contango. This usually happens when there are expectations of increased future demand or higher carrying costs. Contango can be seen in various markets, such as commodities and financial instruments.
Factors Leading to Contango
Several factors contribute to contango. One major factor is high carrying costs, including storage and insurance. When these costs are significant, futures prices tend to be higher. Another factor is market expectations of future price increases. If traders believe prices will rise, they will pay more for futures contracts. Contango often occurs in markets with a surplus supply or low immediate demand.
Implications for Traders and Investors
Contango can impact traders and investors in multiple ways. Holding futures contracts during contango can be costly due to roll costs. These costs arise when extending contracts, as the new contract may be priced higher. Investors might experience reduced returns if they need to roll over contracts frequently. In markets like oil, contango can erode profits for those who need to store commodities.
What is Backwardation?
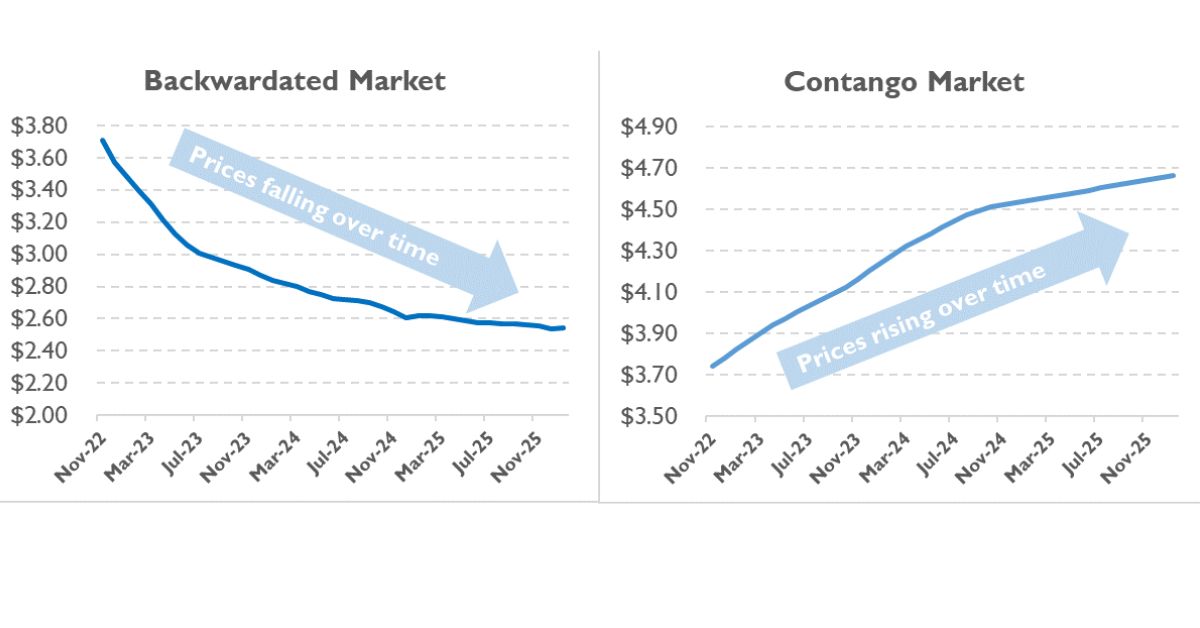
Backwardation is a market condition where futures prices are lower than the spot price. It suggests that traders expect future prices to decrease. For instance, if the current copper price is $6,000 per ton, but futures are $5,800, the market is in backwardation. This condition reflects short-term supply constraints or high immediate demand. Backwardation can be seen in various markets, such as commodities and financial instruments.
Factors Leading to Backwardation
Several factors lead to backwardation. A common factor is a shortage of supply or high immediate demand for the asset. Another factor is the expectation of falling prices in the future. Low storage costs can also contribute to backwardation, as holding the asset is inexpensive. Additionally, short-term market disruptions can create backwardation by affecting supply and demand balances.
Implications for Traders and Investors
Backwardation can benefit traders and investors. Futures contracts may be priced lower than the spot price, providing cheaper entry points. Traders may profit from this price difference. However, backwardation can also signal potential supply issues or market instability. Investors must assess the reasons behind backwardation to make informed decisions.
Which is Better: Contango or Backwardation?
Individual trading strategies and market conditions determine whether contango or backwardation is better. Every market condition has its advantages and challenges, so investment decisions are different. These differences can help traders and investors choose the most suitable strategy.
Contextual Factors
The determination of which is better, contango or backwardation, depends on various factors. These include specific market conditions, investment goals, and risk tolerance. Each market condition offers unique advantages and drawbacks that can affect trading and investment strategies.
Investment Strategies
In a contango market, investors may face higher roll costs when extending futures contracts. This can erode profits, especially in commodity markets where storage costs are high. However, contango can be advantageous for those expecting prices to rise in the future, as they may profit from holding long positions.
In a backwardation market, futures contracts are often cheaper than spot prices, providing opportunities for lower entry costs. This can be beneficial for traders looking to capitalize on short-term price movements. Backwardation can also signal strong current demand or supply constraints, which may present trading opportunities.
Impact on Futures Contracts
Futures contracts in contango are typically priced higher than the spot price. This can lead to increased costs when rolling over contracts. Traders must carefully manage these costs to avoid diminished returns.
Futures contracts in backwardation are priced lower than the spot price. This can result in lower costs for traders and potentially higher returns. However, backwardation might indicate potential supply issues or market volatility that need to be considered.
Market Conditions
This condition often occurs in markets with a surplus of supply or low immediate demand. High carrying costs, such as storage and insurance, can also influence it. Understanding the reasons behind contango is crucial for making informed trading decisions.
This condition is commonly seen in markets experiencing supply shortages or high immediate demand. It can also be a result of low storage costs and short-term market disruptions. Analyzing these factors can help traders and investors anticipate future market trends.
Risk Tolerance and Goals
Contango might be suitable for investors with a higher risk tolerance who believe in long-term price increases. However, they must be prepared for potential roll costs and market volatility.
Low-risk investors might prefer backwardation since it’s cheaper to get in and there are fewer rollover costs. However, they should be cautious of potential market instability and supply issues.
How to Trade During Contango and Backwardation
Trading in backwardation and contango markets requires different strategies to maximize profits. Developing an effective trading plan requires understanding each market condition. Here’s how to navigate these different markets.
Trading Strategies During Contango
Trading in a contango market requires careful planning and strategy to manage the inherent costs and opportunities. Many people take a long-term approach, holding futures contracts in the hope that prices will go up. However, traders must be mindful of the higher roll costs associated with contango.
Some traders use calendar spreads to mitigate these costs by buying near-term contracts and selling longer-term ones. Choosing assets with lower storage costs can also help reduce the financial burden of holding contracts. A good understanding of the underlying factors driving contango is essential for making informed decisions.
Trading Strategies During Backwardation
The backwardation market offers unique opportunities for traders, especially those looking for short-term gains. Futures contracts in a backwardation market are often cheaper than spot prices, so entry points are lower. Traders looking to profit from immediate price movements can take advantage of this.
Continuously rolling over futures contracts is an effective way to take advantage of the lower roll costs. Additionally, traders should consider factors that drive backwardation, such as high current demand or shortages of supply. A backwardation market can maximize returns for traders if they monitor market conditions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Risk Management in Contango and Backwardation
Effective risk management is essential when trading in either contango or backwardation. In a contango market, traders should carefully monitor their roll costs and avoid overextending their positions. Diversifying investments across different assets with varying storage costs can help mitigate risks.
Traders need to watch out for supply issues and disruptions in the market that can lead to sudden price changes in backwardation. Using stop-loss orders and setting clear profit targets can help protect against adverse movements. Furthermore, staying on top of market trends and news can help you adjust strategies as conditions change.
Leveraging Technology and Resources

Traders can navigate contango and backwardation markets effectively with today’s trading platforms. Technical analysis and advanced charting tools can help you spot trends and make data-driven decisions.
These tools can be handy in analyzing the price movements and underlying factors driving contango or backwardation. Additionally, webinars and tutorials can help traders better understand market dynamics and improve their trading strategies.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Trading
The choice between long-term and short-term trading strategies can also influence how traders approach contango and backwardation. Long-term traders in a contango market may focus on assets expected to appreciate over time despite higher roll costs. They might also seek to hedge their positions using options or other derivatives.
Short-term traders may prioritize quick profits in backwardation markets, continuously rolling over futures contracts to maximize returns. Knowing the advantages and challenges of long-term and short-term trading can help traders pick the right strategy based on their goals.
FAQs
Is Contango Bullish or Bearish?
Contango is generally considered a bearish market condition. In contango, futures prices are higher than the spot price. It indicates that traders expect prices to rise over time. However, it also suggests a current oversupply or low demand. Therefore, it can signal a bearish outlook for the near term. Traders may incur higher costs due to the premium on futures contracts. It’s essential to assess market factors carefully.
Contango doesn’t always indicate long-term trends. Understanding market context helps in making informed decisions. By analyzing supply and demand dynamics, traders can better interpret contango. Always consider both current and future market conditions. It helps in developing effective trading strategies.
Is Backwardation Good or Bad?
Backwardation can be seen as both good and bad, depending on your trading perspective. It often indicates strong current demand or supply shortages, which can present opportunities for short-term gains. Traders can buy futures contracts at a lower price, which is beneficial for those looking to profit quickly.
However, backwardation can also signal market instability. Supply issues or high demand can lead to price volatility. Traders must be cautious and prepared for sudden changes. Risk management is crucial in such markets. Understanding the underlying factors driving backwardation is crucial. It helps in making informed trading decisions. By staying informed, traders can effectively navigate backwardation. This balance of opportunity and risk defines backwardation’s impact.
Which is More Common, Contango or Backwardation?
Contango is generally more common than backwardation. In many markets, futures prices tend to be higher than spot prices because of storage costs and other carrying charges. Markets often anticipate future price increases. Contango reflects this expectation. It is typical in stable markets with sufficient supply. Backwardation, on the other hand, occurs less frequently. It often arises from supply disruptions or high immediate demand.
Such conditions are less common. However, backwardation can occur in commodity markets like oil. Both market conditions offer unique trading opportunities. Understanding their frequency helps in strategy development. Traders should analyze current market conditions. It aids in anticipating contango or backwardation scenarios. Always stay informed about market trends.
How to Profit from Contango?
Profiting from contango involves strategic planning and risk management. One standard method is to use calendar spreads, which consist of buying near-term futures and selling long-term futures. Traders can profit from the price difference between contracts. Another approach is to invest in physical commodities and hold these until futures prices rise. This can be more capital-intensive but potentially profitable. Monitoring roll yield is crucial.
Roll costs can erode profits in contango markets. Another option is to use ETFs that track futures markets. These funds often manage roll costs more efficiently. Understanding market trends and factors driving contango is essential. Leverage technology for better analysis. Tools and resources can enhance decision-making. Always stay informed and adaptable. This maximizes potential profits in contango markets.
How to Make Money in Backwardation?
Making money in backwardation can be highly rewarding. This market condition allows traders to buy futures contracts at lower prices than the current spot price. A common strategy is to enter long positions in future contracts. As prices rise, traders can sell them for a profit. Monitoring supply and demand dynamics is crucial. Understanding the factors driving backwardation, such as shortages, can enhance decision-making.
Another approach is to roll over futures contracts continuously. This can help capitalize on the price differences over time. Additionally, investing in commodities directly can be beneficial. Holding physical assets during backwardation may yield significant returns. Consistently implement risk management strategies to protect investments. Being informed about market trends is essential. This can help traders maximize their profits in backwardation.
Conclusion
Choosing between contango and backwardation depends on your trading goals and strategies. Each market condition offers unique opportunities and challenges. By understanding these dynamics, traders can make informed decisions. Effective risk management and staying updated on market trends are essential.
Leverage tools and resources to enhance your trading experience. Adapt your strategies to the specific conditions of contango or backwardation. It will help you maximize your trading potential. With the right approach, you can navigate these markets successfully. Always be prepared and stay informed to thrive in any market environment.