In the ever-changing world of finance, investors who want to maximize their returns must understand the various trading methods available. Three of the most widely used options are spot trading, futures contracts, and options contracts. Each has its advantages and disadvantages, making it essential for traders to understand their differences. In this article, we will explore the key differences between spot vs futures vs options trading. With this knowledge, you will be better equipped to choose the right instrument for your trading needs.
What is Spot Trading?

Spot trading refers to buying or selling a financial instrument for immediate delivery and settlement two business days after the trade date. This type of trading involves exchanging underlying assets at their current market price, like stocks, commodities, or currencies. The spot trading of commodities, equities, and forex takes place in real time, depending on market conditions.
Key Characteristics of Spot Trading
Several vital characteristics distinguish spot trading from other forms of trading. Such as:
Immediate Delivery
Spot trading settles transactions “on the spot,” which means the buyer receives the asset almost immediately after the trade is completed. This immediate settlement distinguishes spot trading from other forms of trading that involve future settlements.
Current Market Prices
Spot trades reflect real-time supply and demand dynamics, reflecting prevailing market prices. Prices in spot trading are transparent and readily available, allowing traders to know the exact price at which assets are bought or sold.
Advantages of Spot Trading
There are several advantages to trading spot currencies, including the following:
Simplicity
One of the primary advantages of spot trading is its simplicity. Beginners can easily understand and execute the process, and traders can easily understand the concept of buying and selling at current market prices without having to deal with complex contracts.
Liquidity
Liquidity is high in many spot markets, especially for major currencies and commodities. Due to this high liquidity, traders can often trade large volumes without significantly impacting the market price.
Transparency
Spot prices provide traders with clear information that helps them make informed decisions. Traders can easily access spot prices, which reflect the actual market conditions, ensuring they know the exact value at which to buy or sell.
Disadvantages of Spot Trading
It is important to note that spot trading has some disadvantages as well. Such as:
Price Volatility
Price volatility is a significant disadvantage of spot trading. Spot trading takes place at current market prices, so traders can experience significant price swings due to price volatility. If the market moves unfavorably, this can lead to substantial losses.
No Leverage
Another disadvantage is the lack of Leverage. Unlike futures or options trading, spot trading usually doesn’t offer Leverage, so traders have to have the total amount to buy. Because of this, traders with smaller capital can’t participate as effectively in the market.
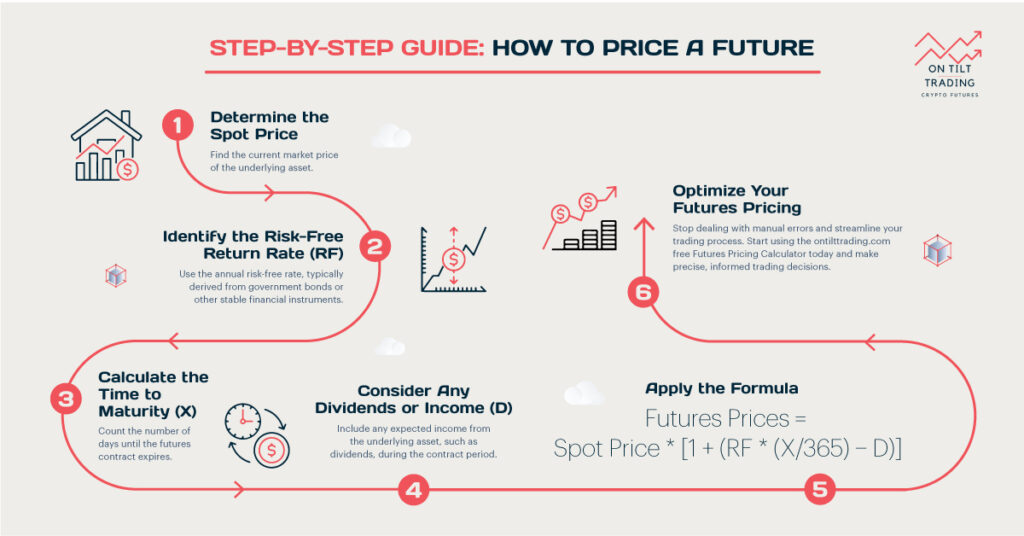
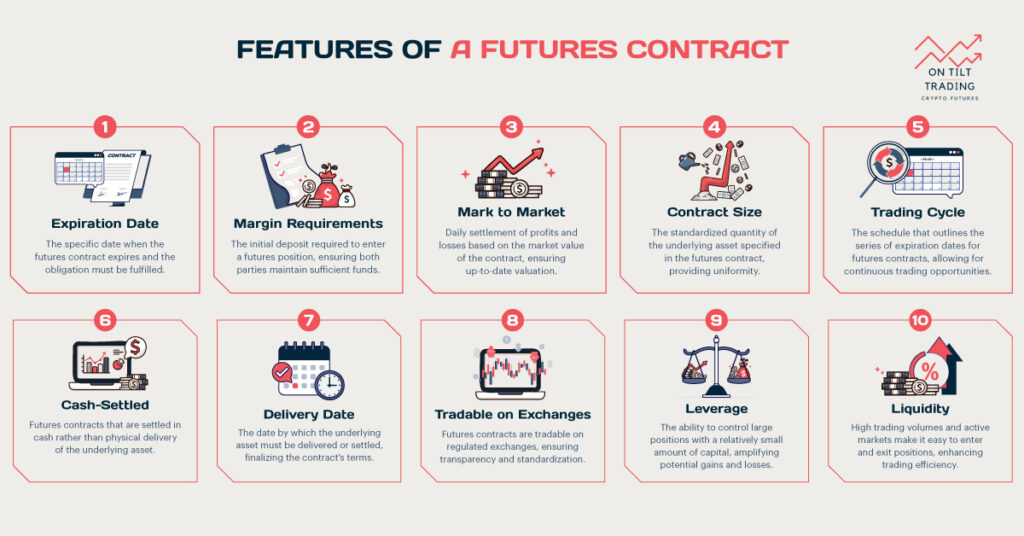
What are Futures Contracts?
Futures contracts are standardized agreements to buy or sell a specific asset at a set price on a future date. They are common in commodities, financial instruments, and currencies. With futures trading, traders can speculate on the future price movements of an asset or hedge against them.
Key Characteristics of Futures Contracts
You should be aware of the following characteristics of futures contracts.
Standardized Contracts
Futures contracts are standardized in terms of quantity, quality, and delivery date. It ensures uniformity in futures exchanges and facilitates trading. Traders know exactly what they are buying or selling, which improves market liquidity.
Future Delivery Dates
Unlike spot trading, futures contracts involve future delivery dates. The buyer and seller agree on a future date for delivery and settlement of the transaction. This enables traders to plan for future requirements and lock in prices.
Advantages of Futures Contracts
It is important to note that futures contracts offer some of the following advantages:
Leverage
Leverage is one of the primary advantages of futures contracts. Traders can control large positions with a relatively small amount of capital, and if the market moves in the trader’s favor, Leverage can increase profits.
Hedging
Futures contracts are commonly used for hedging purposes. Investors and businesses use futures contracts to protect against adverse price changes in the underlying asset. For example, farmers can use futures contracts to lock in prices for their crops, ensuring a predictable income.
Liquidity and Market Efficiency
Especially for major assets like crude oil, gold, and stock indices, futures markets are typically highly liquid. Due to this liquidity, traders can enter and exit positions quickly, minimizing the impact on market prices and providing opportunities for quick profits.
Disadvantages of Futures Contracts
The following are some of the disadvantages of futures contracts:
Risk of Leverage
Leverage can amplify profits, but it can also magnify losses. If the market moves against a trader’s position, they can lose more than their initial investment. Traders without much experience may find futures trading more dangerous than spot trading.
Complexity
Futures contracts are more complex than spot trading. The details of futures markets, like margin requirements, contract specifications, and the impact of economic events, require more expertise, which can be a barrier for new traders.
Obligation to Fulfill Contracts
Unlike options, which give the right to buy or sell an asset but not the obligation, futures contracts require the parties to fulfill their obligations. In other words, the buyer and seller have to complete the deal on the specified date, regardless of market conditions.
What are Options Contracts?

In options contracts, the holder has the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe. In various markets, including stocks, commodities, and currencies, options offer traders flexibility and significant returns.
Key Characteristics of Options Contracts
Several characteristics distinguish option contracts from other types of contracts:
Right But Not Obligation
Essentially, options contracts give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying asset at a specified price. This feature provides flexibility and limits the holder’s risk to the premium paid for the option.
Types of Options (Call and Put)
There are two main types of options: call options and put options. A call option gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset, while a put option gives the holder the right to sell it. When traders expect the asset’s price to rise, they use call options, while when they expect it to fall, they use put options.
Advantages of Options Contracts
It is important to note that options contracts have the following advantages:
Leverage with Limited Risk
Options contracts provide Leverage, allowing traders to control a large position with a relatively small investment. Unlike futures contracts, where losses can surpass the original investment, options have a maximum loss limit of the premium paid.
Flexibility
Options allow traders to customize their trading strategies. With options, traders can speculate on price movements, hedge existing positions, or make money through strategies like covered calls and protective puts. This versatility makes options a powerful tool for both speculative and conservative investors.
Potential for High Returns
Options trading can yield substantial returns if the market moves in your favor. A slight increase in underlying asset price can result in a considerable percentage gain on the option, making it attractive to traders.
Disadvantages of Options Contracts
There are some disadvantages to option contracts, such as the following:
Complexity
Options trading can be complex and requires a solid understanding of strike prices, expiration dates, intrinsic and extrinsic value, and Greeks (delta, gamma, theta, vega). It’s a steep learning curve for novice traders because of this complexity.
Time Decay
One significant disadvantage of options is time decay. If the underlying asset’s price remains stable but the expiration date approaches, the value of options can decrease. Because of this, traders have to be accurate not just in predicting price movements but also in timing them.
Premium Costs
Options require the payment of a premium, which can be costly, especially for longer-term options or those with a high probability of expiring in the money. When multiple trades are executed, these premiums can add up, reducing overall profitability.
Spot vs Futures vs Options Trading: Key Differences
The differences between spot vs futures vs options trading are crucial for traders looking to make informed decisions. The characteristics of each instrument make them suitable for different trading strategies and risk profiles.
| Feature | Spot Trading | Futures Contracts | Options Contracts |
| Settlement and Delivery | Immediate, typically within two business days | Future date, specified in the contract | Depends on the exercise of the option |
| Leverage | No leverage, full capital required | Significant leverage, small capital required | Leverage with limited risk, premium paid |
| Risk | Exposed to immediate price volatility | High risk due to leverage, potential for margin calls | Limited to premium paid, complex factors like time decay |
| Complexity | Simple and straightforward | More complex, involves margin requirements and contract specs | Most complex, involves strike prices, expiration, and Greeks |
| Use Cases | Ideal for beginners and straightforward transactions | Used for speculation and hedging, locking in future prices | Used for various strategies, speculation, hedging, income generation |
Settlement and Delivery
Spot trading settles transactions immediately, usually within two business days. A buyer receives the asset almost instantly, and the trade is completed at the current market price. The immediate settlement makes spot trading simple and straightforward.
Futures contracts have a future delivery date, so the buyer and seller agree on a specific date for the asset to be delivered. Futures contracts are helpful for hedging price fluctuations since they lock in prices for future transactions.
Options give you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price within a certain period of time. The settlement depends on whether the holder decides to exercise the option. When the option is exercised, the trade is settled according to the contract terms; otherwise, it expires worthless.
Risk and Leverage
Spot trades don’t usually offer Leverage, so traders need to invest the whole amount. This limits potential gains but also reduces losses. Traders are exposed to the market’s immediate price volatility.
With futures contracts, traders can control large positions with a relatively small amount of capital. It can enhance profits, but it can also magnify losses, making futures trading more risky. Traders must manage margin requirements and potential margin calls.
Options provide Leverage with limited risk. The maximum loss is limited to the premium paid for the option, making it less risky than futures contracts. Time decay and volatility are two factors that affect an option’s value, making options trading complex.
Use Cases
Spot trading is ideal for traders looking for simplicity and immediate transactions. Investors who want to buy and hold assets or who prefer straight-forward buying and selling at current market prices use it.
Futures are widely used for speculation and hedging. Speculators use futures to bet on price movements without having to own the underlying asset. Hedgers, such as farmers or corporations, use futures to lock in prices and protect against adverse price movements.
Options are flexible and can be used for a variety of strategies, including speculation, hedging, and income generation. Traders use options to speculate on price movements, hedge existing positions, or generate income through strategies such as covered calls and protective puts.
Complexity
Spot trading is the least complex of the three instruments. It involves straightforward transactions at current market prices, making it accessible for beginners.
Leverage, margin requirements, and contract specifications make futures trading more complex. It requires a higher level of knowledge and expertise.
Options trading is the most complex, with strike prices, expiration dates, intrinsic and extrinsic values, and Greeks (delta, gamma, theta, vega). This complexity necessitates a solid understanding and a steep learning curve.
Read More: Crypto Futures vs Spot Calculator App: A Complete Guide
Conclusion
Knowing the difference between spot trading, futures contracts, and options contracts is key to making informed trades. Each has advantages and drawbacks, suitable for different strategies and risk profiles. Choosing the right instrument can help traders align their activities with their goals.