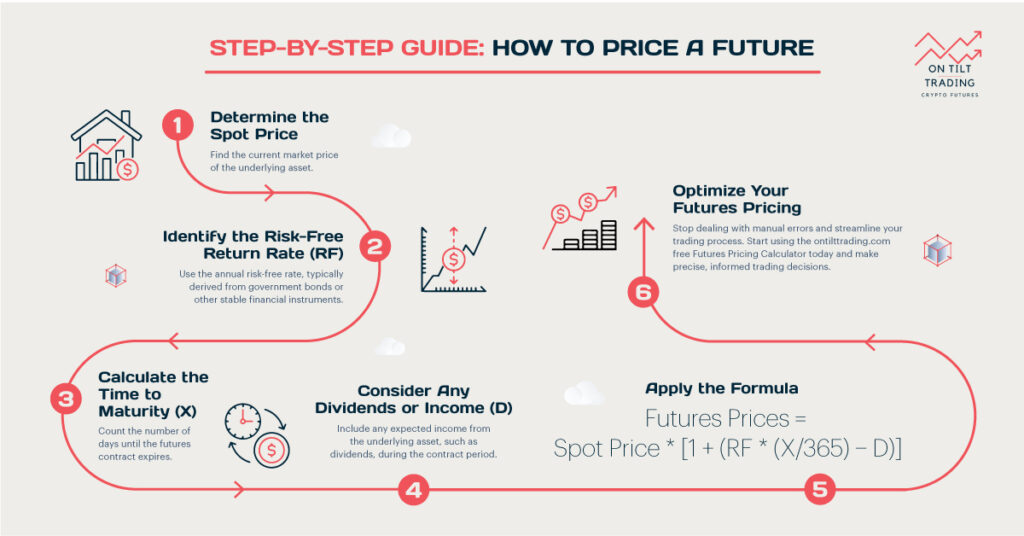
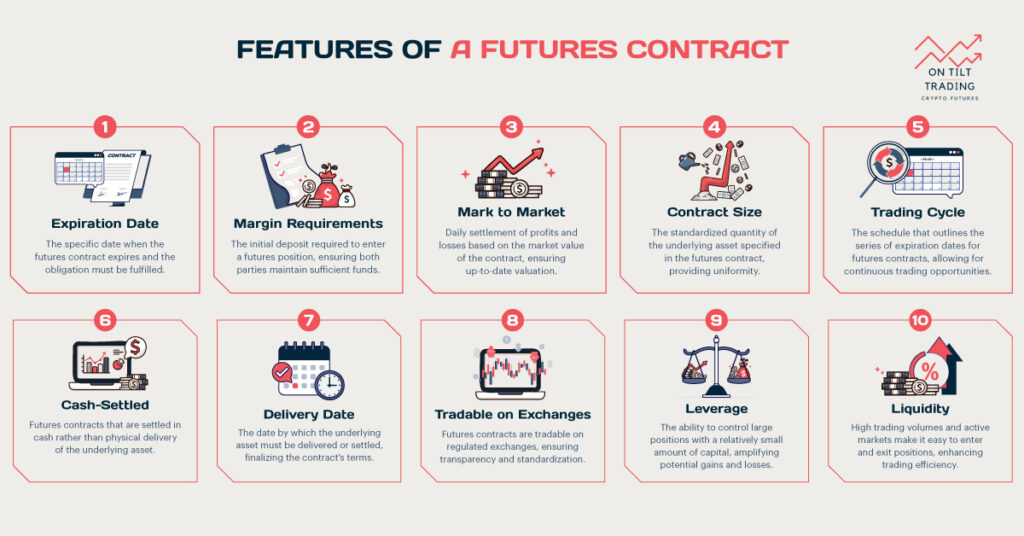
Trading options like futures and options can significantly enhance your profits. Investors and traders can capitalize on price movements in various assets through options and futures contracts. Understanding the differences between futures vs options profit is crucial to managing risk and optimizing profitability.
What are Futures Contracts?
At their core, futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell a specified asset at a predetermined price on a future date. Futures exchanges provide liquidity and transparency to participants in the market. Futures contracts bind both parties to fulfill their terms at expiration, regardless of current market conditions.
It involves predicting the future price direction of the underlying asset. Traders can take either a long position (buying) if they anticipate an increase in price or a short position (selling) if they expect a decline. The ability to profit from futures trading lies in correctly forecasting price movements and timing the market effectively. To maximize your profit by investing in futures contracts you should consider a reliable trading platform.
Example of Profit Scenario with Futures
A trader believes crude oil prices, currently trading at $70 per barrel, will rise over the next three months. They decide to buy a futures contract for 100 barrels of oil at $70 per barrel, with a three-month expiration date. If the price of oil increases to $80 per barrel by expiration, the trader can sell the futures contract at the current market price of $80, realizing a profit of $10 per barrel ($80 – $70).
Benefits of Futures Contracts
- Futures contracts typically require a fraction of the contract value as the initial margin. It allows traders to control larger positions with less capital.
- Futures contracts are widely used to hedge against price fluctuations. It enables businesses to manage risk exposure in volatile markets.
- The establishment of futures exchanges ensures robust liquidity, facilitating efficient price discovery.
What are Options Contracts?
Options contracts are derivative instruments that derive their value from an underlying asset, such as stocks, commodities, or indices. They provide flexibility to traders by offering two primary types:
- Call Options: Give the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price).
- Put Options: It allows the holder to sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) before or at expiration.

Options trading involves speculating on the future price direction of the underlying asset. Unlike futures contracts, options provide the flexibility to choose whether to exercise the contract based on market conditions. This feature makes options particularly attractive for hedging strategies and speculative trades.
Example of Profit Scenario with Options
Consider a trader who purchases a call option on Company XYZ stock, which is currently trading at $100 per share. The call option has a strike price of $110 and expires in three months. If Company XYZ’s stock price rises to $120 by expiration, the trader can exercise the call option, buying the stock at $110 and immediately selling it at the market price of $120. The company made $10 per share ($120 – $110).
Alternatively, if the stock price remains below $110 by expiration, traders can let the option expire without exercising it, limiting their losses to the premium paid.
How to evaluate trade profitability accurately? Our On Tilt Trading ROI Calculator helps you assess and optimize your portfolio, identifying high-performing investments. Boost your trading success now!
Benefits of Options Contracts
- The maximum loss in options trading is limited to the premium paid for the contract
- Options can be used for various trading strategies, including speculation, hedging, and income generation.
- Unlike futures contracts, options offer the flexibility to choose whether to exercise the contract based on market conditions.
Futures vs Options Profit: In-depth Comparison
Risk and Reward Profiles
One of the primary distinctions between futures vs options profit lies in their risk and reward profiles.
As obligations to buy or sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price, futures contracts carry unlimited profit potential if the market moves in favor of the trader’s position. However, they also entail substantial risk, as losses can exceed the initial margin requirement due to leverage.
Options provide the right but not the obligation to buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying asset. They offer limited downside risk, capped at the premium paid for the option contract. While potential profits from options can be substantial, they are typically lower than futures due to the premium cost and the fact that options expire.
Leverage and Margin Requirements
Leverage plays a crucial role in both futures and options trading. Futures contracts require an initial margin, which is a fraction of the contract’s total value. This leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller capital outlay. However, leverage magnifies both potential gains and losses.
Options also involve leverage but to a lesser extent compared to futures. The premium paid for the option contract represents the trader’s maximum potential loss, providing a defined risk exposure. It is crucial to consider expiration dates and volatility when trading options.
Strategic Flexibility
The strategic flexibility offered by futures and options differs significantly. Futures are straightforward in their approach, focusing on price speculation and hedging strategies. Traders must manage their positions actively to capitalize on market movements and mitigate risk exposure.
Options provide strategic flexibility, allowing traders to implement various strategies based on market conditions. From simple directional bets (calls and puts) to complex strategies like spreads and straddles, options cater to diverse trading objectives and risk preferences.
Practical Examples and Profit Strategies
A futures trader might profit from accurately predicting a commodity’s price increase over time, leveraging margin to amplify gains.
An options trader might use a combination of call-and-put options to hedge against market volatility. It is possible to profit from price movements without committing to buy or sell the underlying asset.
Maximizing Profit in Futures or Options Trading
Achieving success in futures vs options trading requires a strategic approach that balances risk management with profit potential. Whether you’re trading futures contracts or options contracts, here are key strategies to help maximize your profitability:
Market Dynamics
You should thoroughly research and understand the market before you start trading. Study historical price movements, current trends, and factors influencing the asset’s price. A solid grasp of market dynamics enhances your ability to predict price movements and make informed trading decisions.
Develop a Clear Trading Plan
Create a well-defined trading plan that outlines your goals, risk tolerance, and entry/exit strategies. Determine the types of contracts you’ll trade (futures or options), preferred trading timeframes, and the amount of capital you’re willing to risk per trade. A disciplined approach helps mitigate emotional decision-making and improves consistency in trading.
Utilize Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Combine technical analysis (chart patterns, indicators) with fundamental analysis (economic data, company earnings) to identify trading opportunities. Technical analysis helps pinpoint entry and exit points based on price patterns and market trends, while fundamental analysis provides insights into broader market conditions and potential catalysts.
Implement Risk Management Strategies
Effective risk management is crucial for long-term success. Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and protect profits. Determine your risk-reward ratio for each trade to ensure that potential gains outweigh potential losses. Additionally, diversify your portfolio to spread risk across different assets or sectors.
Employ Strategic Position Sizing
Adjust your position size based on the level of risk and your trading strategy. Avoid overleveraging by adhering to responsible position-sizing principles. As your trading capital grows, consider scaling up your positions gradually while maintaining risk control.
Explore Options Strategies
In options trading, explore various strategies beyond simple calls and puts. Strategies like covered calls, protective puts, straddles, and spreads can be used to capitalize on different market conditions (bullish, bearish, or neutral). Each strategy has its own risk-reward profile, so choose one that aligns with your market outlook and risk tolerance.
Stay Informed and Adapt
Stay updated on market news, economic events, and geopolitical developments that could impact your trades. Remain flexible and adapt your trading strategies as market conditions evolve. Continuous learning and adjustment are key to staying competitive in dynamic financial markets.
Final Words
Futures might require more money upfront due to margin requirements, while options usually have a lower initial cost (the premium). Futures can require additional funds if the market moves against you, whereas options only require the initial premium. Making the right choices is the key to achieving success. To do that you have to utilize the right tools. It will help you to make the right decisions.