A future contract is essential when you want to lock in a price for a future purchase or sale. Investors use futures to manage risks associated with price fluctuations in commodities like oil or crops. Companies use them to secure predictable raw material costs. Traders engage in futures to speculate on future price movements of stocks or currencies. If you don’t have a proper idea about how futures contracts work, then you are at the right place. We will explore the features of futures contract to help understand.
Example of Futures Contract
Futures Contract also applies to Crypto traders. Here is an example: let’s say a trader believes Bitcoin’s price will rise in the coming months. Instead of buying Bitcoin directly, they decide to enter into a Bitcoin futures contract. Imagine the current price of Bitcoin is $30,000. The futures contract they choose expires in three months. The trader buys a Bitcoin futures contract at $30,000 for one Bitcoin. This contract obligates them to buy one Bitcoin at $30,000 in three months, regardless of its market price.

If, after three months, the price of Bitcoin has risen to $40,000, the trader benefits. Because he can still buy Bitcoin at the lower contracted price of $30,000 and then sell it immediately at the higher market price of $40,000. He will be making a profit of $10,000 per Bitcoin.
On the other hand, if the price of Bitcoin falls to $25,000 in three months, the trader is still obligated to buy it at $30,000 under the futures contract. It will result in a loss of $5,000 per Bitcoin. But make sure to use a reliable crypto platform for trade execution.
Features of Future Contracts
Anyone who trades or uses futures contracts must understand the features of future contracts. These features affect trading strategies, risk management, and potential profits or losses. Let’s try to understand:

1. Expiration
Every future contract has an expiration date. This is the final trading day for the contract. After this date, the contract will be settled based on exchange rules.
2. Contract Size
Exchanges set a standard amount of the underlying asset for each contract. This amount is the contract size. It defines the trading unit. For example, One E-mini S&P 500 futures contract represents $50 times the S&P 500 Index value.
3. Initial Margin
Traders must deposit a minimum amount of collateral to open a futures position. This deposit is the initial margin. Exchanges set this amount based on the contract’s volatility.
For example, the initial margin for an E-mini S&P 500 futures contract might be $6,000. Initial margins vary from commodity to commodity as well as from time to time. It mainly depends on the volatility of the contract. For high volatility, you have to pay a higher margin.
4. Price Quotation
The price quotation is how the contract’s price appears in trading systems. It may differ from the actual contract size. It is often determined by industry practices and conventions and varies from the trading size of a contract.
Example: Crude oil futures are quoted in dollars per barrel, even though one contract represents 1,000 barrels.
5. Tick Size
The tick size is the smallest price increment allowed for a futures contract. It varies by contract and exchange. The Tick value depends on the size of the Tick and the contract. Example: For E-mini S&P 500 futures, the tick size is 0.25 index points.
6. Tick Value
The tick value is the monetary value of one tick move. It depends on the tick size and contract size. Here is the formula of calculating Tick Value:
Tick Value = Tick Size × Contract Size
Example: For E-mini S&P 500 futures: Tick Value = 0.25 × $50 = $12.50
7. Mark to Market
Mark to market refers to calculating and valuing open positions based on predefined rules and regulations. Exchanges perform daily mark-to-market calculations. This process adjusts the value of open positions to reflect current market prices. It helps manage counterparty risk.
Formula: Daily P&L = (Closing Price – Previous Day’s Closing Price) × Contract Size × Number of Contracts
If you hold one long E-mini S&P 500 contract and the index rises 10 points: Daily P&L = 10 × $50 = $500
8. Delivery Date
The delivery date is when sellers must deliver the underlying asset to buyers. Many traders close their positions before this date to avoid physical delivery. Example: A July 2024 wheat futures contract might have a delivery date of August 15, 2024.
7. Daily Settlement
Exchanges perform daily settlements. They credit or debit traders’ accounts based on daily price movements. This process ensures all parties can meet their obligations.
Formula: Settlement Amount = (Settlement Price – Previous Day’s Settlement Price) × Contract Size × Number of Contracts
Example: If you hold two short gold futures contracts and the settlement price rises $5 per ounce: Settlement Amount = $5 × 100 oz × 2 contracts = $1,000 debit
Futures contracts allow traders to control a large position with relatively little capital. Traders can use futures to speculate on the direction of market prices. Futures markets tend to be very liquid, meaning there are many buyers and sellers. This liquidity makes it easier to enter and exit positions. But you will need time to monitor the market and understand the upcoming ups and downs before making a future contract. Besides, beginners may find the process of making future contracts difficult.
The expiration date is one of the most important aspects of futures contracts for traders to monitor. After an expiration date, the price of a contract can rapidly decline, even becoming worthless. The investors roll forward their futures contracts to a later date when the expiration date gets closer.
Different Types of Future Contracts
You can use future contracts to set the price of any type of asset or commodity. To help you understand, we have compiled a list of the most frequently traded types of futures contracts:
- Commodity futures: These involve physical goods like oil, gold, wheat, or livestock. Farmers and manufacturers often use them to lock in prices.
- Stock index futures: These are based on stock market indexes like the S&P 500. Investors use them to bet on overall market movements.
- Currency futures: These contracts involve exchanging one currency for another at a future date. They help businesses manage foreign exchange risk.
- Interest rate futures: These are based on interest-bearing assets like government bonds. They’re used to hedge against interest rate changes.
- Precious metal futures: These involve metals like gold, silver, and platinum. They’re popular with investors looking for a safe haven.
- Energy futures: These cover oil, natural gas, and electricity. They help energy companies manage price volatility.
- Agricultural futures: These involve crops like corn, soybeans, and coffee. Farmers use them to protect against price drops.
- Weather futures: These are based on weather conditions. They help businesses affected by weather, like ski resorts or utility companies.
- Real estate futures: These are linked to property values in specific areas. They’re used to manage real estate market risks.
- Cryptocurrency futures: These are newer contracts based on digital currencies like Bitcoin. They allow speculation on crypto price movements. We have already provided an example of a crypto future contract.
Are Future Contracts Good Investments?
Future contracts can be attractive investments for those wishing to manage risks or capitalize on price movements.
One of the primary advantages of futures contracts is their ability to hedge against price volatility. For example, a farmer may use futures contracts to lock in a price for their crops before harvest. It helps them protect against price drops.
Moreover, futures contracts provide opportunities for speculation. Traders can profit from anticipated price movements without owning the underlying asset. However, this leverage also increases the risk of significant losses if adverse market movements occur. Are you unsure when your trades will be profitable? Our On Tilt Trading Break-Even Calculator pinpoints the exact moment you start making profits. Set realistic goals and manage risks effectively. Optimize your trading now and win!
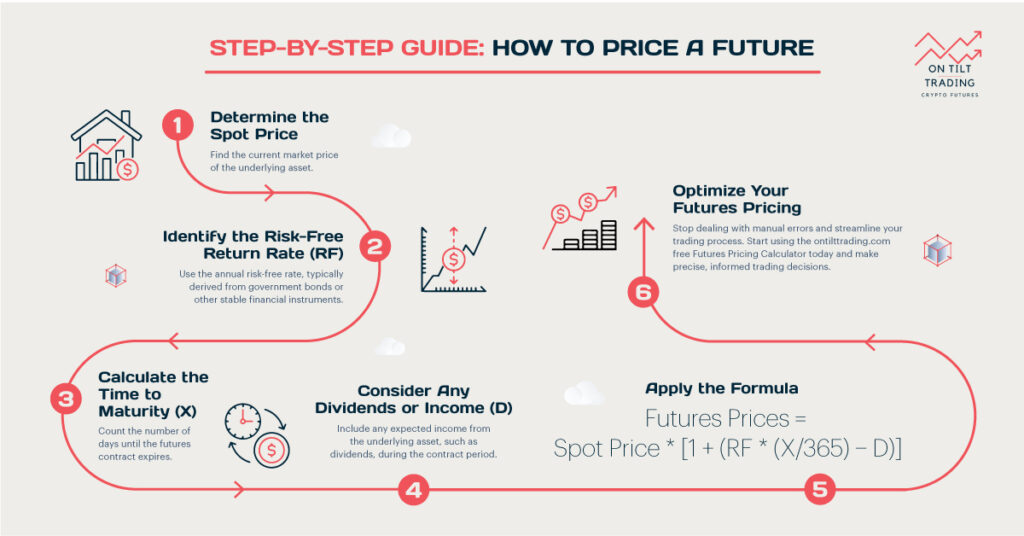
Read More: How to Price a Future
Final Words
Any trader involved in futures contracts needs to understand the features in detail. Each feature plays a vital role in how these contracts function and how they can be used effectively for hedging, speculation, and investment. Make sure you can handle the risks related to the contract. As a trader, you can make more informed decisions and manage risks and rewards better by undertaking the features of future contracts.