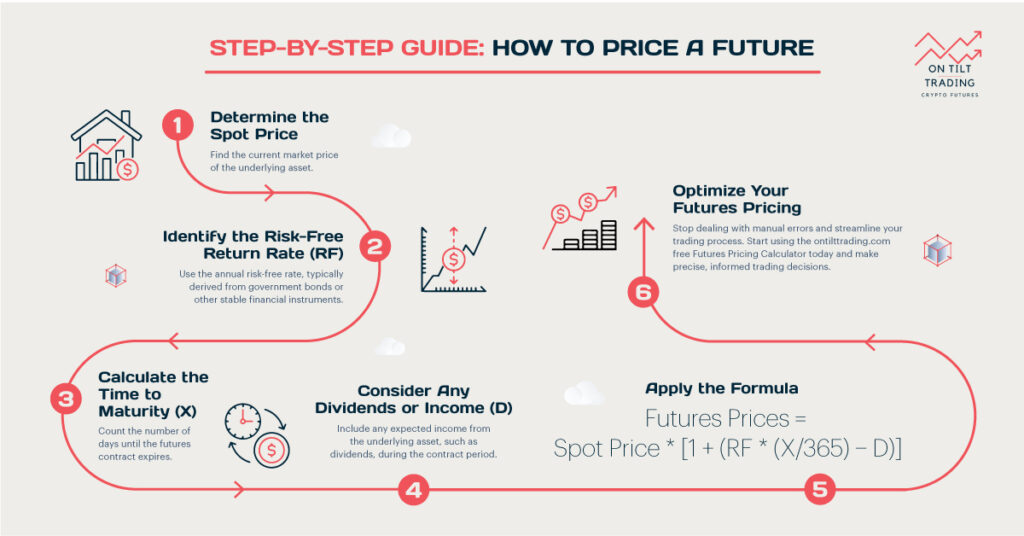
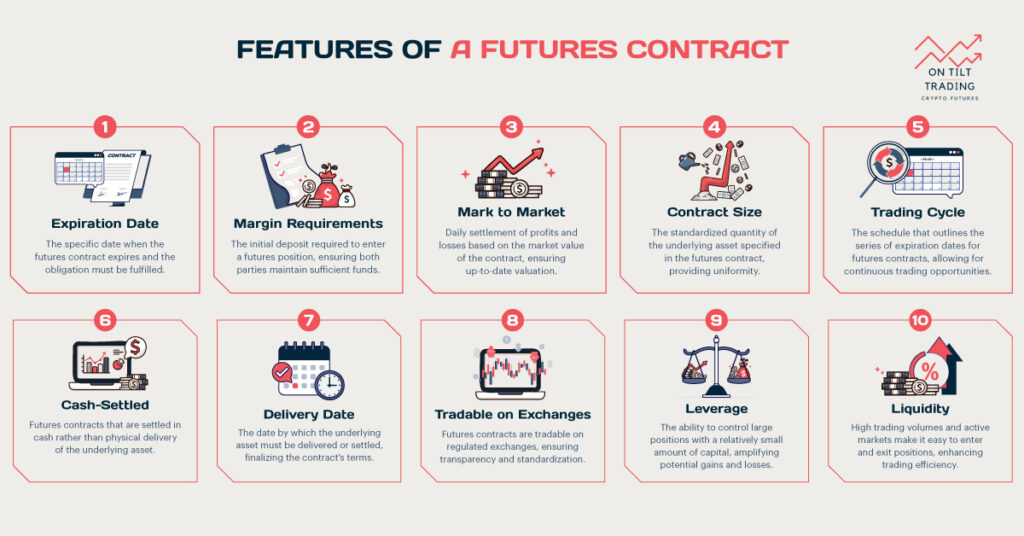
Futures trading is a powerful financial tool that allows traders to speculate on asset prices in the future. You can significantly improve your trading success if you know when to buy or sell futures. In this article, we will guide you through the key factors and strategies for making informed decisions.
Trading futures at the right time can help you stay ahead of the market and maximize your profits. Market indicators, economic factors, and strategic approaches can help you time your futures trades better. With this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn how to make profitable futures trading decisions.
What is Futures Trading?

Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell assets at a set future date. They specify both price and quantity. Futures can involve commodities, financial instruments, or currencies. They are standardized and traded on regulated exchanges.
A long position means agreeing to buy the asset in the future. Conversely, a short position means agreeing to sell the asset. Understanding these concepts is crucial for futures trading.
Types of Futures Contracts
- Commodity Futures: These involve physical goods like oil, gold, and wheat. Traders speculate on the future prices of these commodities.
- Financial Futures: These involve financial instruments such as stock indices and interest rates. They allow traders to speculate on financial market movements.
- Currency Futures: These contracts involve foreign currencies, allowing traders to speculate on future exchange rate movements.
- Interest Rate Futures: These involve interest-bearing instruments, helping traders hedge against interest rate fluctuations.
How Futures Markets Work
Futures are traded on exchanges that provide a regulated marketplace and ensure transparency and liquidity. To trade futures, margin requirements must be met. This involves depositing a percentage of the contract’s value as collateral. Clearinghouses play a crucial role in futures markets.
They guarantee the performance of each contract and mitigate counterparty risk. Settlement mechanisms ensure contracts are honored at expiration. Due to these structures, futures markets operate efficiently.
Factors Influencing Futures Prices
Trading futures successfully requires understanding what influences prices. Supply and demand dynamics, economic indicators, market sentiment, and government policies are all crucial. By analyzing these factors, traders can make better buying or selling decisions.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
Supply and demand significantly impact futures prices. High demand or low supply drives prices up, while low demand or high supply drives prices down. Seasonal variations can also affect supply and demand.
For example, agricultural products often see price changes based on harvest times. Weather conditions also influence commodity futures, and natural disasters can disrupt supply chains and impact prices.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide insights into market conditions. GDP growth rates indicate overall financial health. High GDP growth can boost demand for various commodities, and inflation rates are crucial for futures trading.
High inflation often leads to higher commodity prices. Employment data can influence futures markets. Strong employment numbers can boost consumer spending and demand for goods.
Market Sentiment and Speculation
The market sentiment reflects investors’ overall attitude. Positive sentiment can drive prices up, while negative sentiment can drive prices down.
Speculative trading activities can significantly impact futures prices. Traders often react to news and events, causing price fluctuations. Understanding market sentiment is critical to successful futures trading.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations can affect futures prices. Tariffs and trade policies impact international trade and commodity prices. Changes in monetary policy, such as interest rate adjustments, can influence financial futures.
Regulatory changes can also affect market dynamics. Staying informed about policy changes is crucial for futures traders.
Strategies for Buying Futures

Futures trading requires a variety of strategies tailored to different market conditions. Each plan offers unique advantages and risks. If traders understand and apply these strategies, they can help make informed buying decisions.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves examining economic indicators and financial statements. Traders use this to evaluate the intrinsic value of assets. Understanding supply and demand is crucial. For example, crop reports predict agricultural commodity prices.
Central bank policies provide insights into interest rate futures. By analyzing these factors, traders make informed buying decisions. Economic data helps identify potential price movements. This analysis requires staying updated with financial news.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis focuses on price charts and trading volumes. Traders use historical data to predict future price movements. Standard tools include moving averages, RSI, and MACD. Identifying trends and patterns is vital. For instance, a rising moving average indicates an upward trend.
Conversely, a falling moving average signals a downtrend. Support and resistance levels are also crucial. Technical analysis helps traders time their futures purchases. This approach relies on market psychology and patterns.
Trend Following
Trend following involves trading in the direction of the current market trend. This strategy aims to capture gains by riding market momentum. Traders use tools like moving averages and trend lines. For example, buy when the price is above the moving average.
Sell when the price falls below the moving average. Trend following requires discipline and patience. This strategy works best in trending markets. Traders must avoid false signals and whipsaws.
Contrarian Investing
Contrarian investing involves going against prevailing market trends. This strategy is based on the belief that markets often overreact. Contrarian traders buy undervalued assets and sell overvalued ones. For example, they buy commodities during a price dip.
The best time to sell them is when the prices are high. This approach requires a strong understanding of market fundamentals. Contrarian investing is risky but can be rewarding. It requires patience and a long-term perspective.
Hedging
Hedging protects against adverse price movements by taking an offsetting position in a related futures contract. For instance, a farmer might sell futures to lock in crop prices. This strategy helps manage risk and ensure predictable revenue.
Businesses and investors commonly use hedging to mitigate potential losses. Hedging can be complex and require careful planning, but it is a vital tool for managing financial risk.
Scalping
Scalping is a short-term trading strategy. It involves making multiple trades throughout the day. The goal is to profit from small price movements. Scalpers often use technical analysis and real-time data. Quick decision-making and discipline are crucial.
This strategy requires a high level of concentration and quick reflexes. Scalping involves low profit margins per trade. Successful scalping demands efficient execution and low transaction costs.
Strategies for Selling Futures

To sell futures effectively, you must tailor your strategies to the market conditions. It helps traders manage risk and identify optimal selling points.
Identifying Overbought Conditions
Identifying overbought conditions is essential for effective selling. Traders utilize technical indicators to assess market sentiment. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is commonly used; readings above 70 signal overbought conditions. The Stochastic Oscillator also helps indicate overbought situations.
Recognizing market cycles aids in predicting potential reversals. Understanding these cycles allows traders to make informed selling decisions. Monitoring price trends is crucial for spotting overbought conditions.
Fundamental Triggers for Selling
Fundamental triggers can signal optimal selling times. Negative economic news often leads to declining prices. Rising unemployment rates can negatively impact market sentiment, and poor company performance significantly affects stock futures.
Earnings reports that fall short of expectations may prompt immediate selling. Traders should stay informed about economic indicators and corporate performance. Awareness of geopolitical events can also influence selling decisions.
Hedging Against Price Declines
Hedging is a vital strategy for protecting against price declines. Traders hedge long positions by taking short futures contracts, which helps lock in profits and mitigate potential losses.
For instance, if a trader holds long oil futures, selling them can protect against price drops. Hedging provides a safety net in volatile markets, allowing traders to maintain stability amid price fluctuations. Effective hedging requires careful analysis of market conditions.
Speculative Short Selling
Speculative short-selling allows traders to profit from anticipated price drops. This strategy involves borrowing futures contracts and selling them at current prices. If prices decline, traders can repurchase the contracts at a lower cost.
This approach requires diligent market analysis and timing. Successful speculative short-selling hinges on accurate predictions. Traders must act quickly before prices fall significantly. While potentially lucrative, this strategy carries inherent risks.
Timing the Market: When to Buy or Sell Futures

Timing the market is crucial for successful futures trading. Knowing when to buy or sell can significantly impact your returns. Staying informed and using various strategies can help traders maximize their profits.
Market Timing Strategies
Effective market timing strategies are essential for successful futures trading. Utilizing economic calendars helps traders anticipate market movements, and monitoring news and events allows traders to react quickly to market changes.
For example, unexpected geopolitical events can lead to rapid price fluctuations. By staying informed, traders can make timely buying and selling decisions. Developing a proactive approach is vital to maximizing trading opportunities.
Seasonal Trends
Seasonal trends significantly influence commodity and financial futures. Historical patterns reveal that certain commodities peak during specific times of the year. For instance, agricultural futures often rise before harvest due to increased demand.
Trading seasons allow traders to capitalize on price movements. Financial futures may also exhibit seasonal behavior influenced by fiscal quarters or economic cycles. Analyzing historical data helps traders anticipate these trends.
Risk Management Techniques
Implementing risk management techniques is vital for future trading success. Setting stop-loss orders helps limit potential losses by automatically selling at predetermined levels. This strategy protects traders from significant downturns in their positions.
Diversifying futures positions across different markets reduces risk exposure. Spreading investments helps traders mitigate the effects of adverse price movements. Effective risk management safeguards capital and enhances overall trading performance.
Leveraging Technology
Leveraging technology can significantly improve trading efficiency. Advanced trading platforms offer tools for analyzing market data in real time. Traders can utilize algorithms to execute trades based on predefined criteria. These automated systems can enhance accuracy and speed. Real-time data feeds provide up-to-the-minute information, allowing for informed decision-making. Utilizing technology helps traders stay competitive in the fast-paced futures market.
FAQs
What is the best time to trade futures?
The best time to trade futures varies by market and asset. Generally, trading during peak hours ensures higher liquidity. For commodities, early morning sessions often see increased activity. For stock index futures, the first hour after the market opens is ideal.
Additionally, traders should consider major economic releases that can cause volatility. Monitoring global market hours can also inform trading times. Ultimately, the best trading time aligns with your strategy and the specific futures market you are interested in.
When should you sell futures contracts?
You should sell futures contracts when market conditions signal a price decline. It could occur during overbought conditions identified through technical indicators like the RSI. Selling before negative economic news can help protect profits. Additionally, if you identify fundamental triggers, such as poor company performance, it’s wise to act.
Seasonal trends may also indicate optimal selling times, especially in commodity markets. Setting clear exit strategies and stop-loss orders can enhance your decision-making. Ultimately, timing your sales effectively can maximize your returns and minimize losses.
Read More: Which Is Better Contango Or Backwardation?
The Takeaway
Ultimately, understanding when to buy and sell futures is key to success. The right strategies, analysis of market conditions, and knowledge of economic indicators allow traders to make timely decisions.
Factors like supply and demand, seasonal trends, and market sentiment all play significant roles. Mastering the art of timing will improve your future trading performance and profitability. Make sure you have the right tools and knowledge to navigate this dynamic landscape.